The Gist
- Conversational AI is now core CX infrastructure. It has moved beyond website chatbots into assistants and platforms that carry context, connect to business data and support multi-step customer and employee workflows.
- LLMs + orchestration changed what “conversation” means. Modern systems interpret intent, manage dialogue across turns and channels and generate responses dynamically — with guardrails and escalation when confidence is low.
- Multimodal and omnichannel experiences are raising expectations. Customers increasingly engage through text, voice, and images in one continuous thread, making continuity, trust and measurement essential to scale.
When people think of conversational AI, their first image is often a chatbot on a business website. A small chat window appears in the corner of the screen, offering help from a digital assistant. That is still one expression of conversational AI, often described as a conversational AI chatbot, but it no longer captures the full picture.
Today’s conversational AI shows up in far more places and plays a far more active role. It powers virtual assistants that can reason through complex requests, customer service systems that understand context across channels, and AI tools that support employees, create content, and even provide emotional or social interaction. In many cases, these systems are no longer limited to scripted responses or narrow tasks. They can carry on fluid, multi-turn conversations that adapt in real time.
Conversational AI has become a foundational layer in how people interact with digital systems, extending far beyond simple chat interfaces. So what is conversational artificial intelligence today, and how did it evolve to this point? What does a conversation with AI actually look like in a world that is shaped by large language models (LLMs) and multimodal systems? And how is this technology reshaping the relationship between businesses and the people they serve?
Table of Contents
- What Is Conversational AI?
- Frequently Asked Questions About Conversational AI
- The History of Conversational AI: From Chatbot to Present
- How Conversational AI Works
- The Advancement of Conversational AI
- Conversational AI vs. Traditional Chatbots
- Benefits of Conversational AI for Businesses and Customers
- Common Use Cases for Conversational AI
- Multimodal AI: Expanding Conversational Capabilities
- People Trust Conversational AI Solutions
- Challenges and Limitations of Conversational AI
- Conversational AI Is Trusted — but Is It Safe?
- Businesses (and People) Rely on Omnichannel Conversational AI
- How to Measure Conversational AI Success
- Conversational AI Facilitates Hyper-Personalization
- Conversational AI Is Part of Our Daily Lives
What Is Conversational AI?
Conversational AI is technology that enables people to interact with computers using natural language through text, voice or other conversational inputs. Instead of relying on fixed scripts, modern conversational AI can interpret intent, maintain context across multiple turns and generate responses that adapt to what a user is trying to accomplish.
In practice, conversational AI can power everything from customer service assistants and voice systems to employee support tools and multimodal experiences that incorporate images and audio. It’s often powered by large language models, but strong conversational AI also depends on orchestration, data access and guardrails that keep interactions accurate and appropriate.
Frequently Asked Questions About Conversational AI
Key questions CX, digital experience and business leaders ask as conversational AI moves from chatbots to core infrastructure.
The History of Conversational AI: From Chatbot to Present
To understand how conversational AI works, it helps to look beyond the interface and examine the systems that interpret intent, manage dialogue and generate responses. The standard definition of conversational AI is a combination of technologies — machine learning (ML) and natural language processing (NLP) — that allows people to have human-like interactions with computers.
How Conversational AI Works
Conversational AI looks simple on the surface, but most systems rely on multiple layers working together to understand a request and respond appropriately:
- Language understanding. Models interpret what the user means, not just the words they type or say.
- Conversation management. The system tracks context across multiple turns and decides what to do next.
- Knowledge and data access. Useful answers often require retrieving policies, account details or order information from business systems.
- Response generation. The system produces an answer, recommendation or action confirmation in natural language.
- Safety and escalation. Guardrails manage sensitive topics, reduce errors and route high-stakes issues to humans.
Organizations get the best outcomes when they treat conversational AI as an orchestrated experience — not just a model — with clear rules for data use, confidence thresholds and human handoffs. To understand this further, let’s look at the evolution of conversational AI.
Key Milestones in Conversational AI: From Scripts to Multimodal Systems
This table outlines how conversational AI evolved from early scripted chatbots into modern, large language model–driven and multimodal systems.
| Era | System or Approach | Primary Capability | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1960s | ELIZA | Rule-based pattern matching | Demonstrated how limited scripts could still feel conversational in narrow contexts |
| 1970s | PARRY | State-aware scripted dialogue | Introduced early concepts of conversational context and behavioral modeling |
| 1990s | ALICE (AIML) | Structured intent and response templates | Scaled chatbot interactions on the web but remained limited to predefined logic |
| 2018–2023 | LLM-powered chat interfaces | Dynamic, context-aware language generation | Marked the transition from scripted bots to adaptive conversational systems |
| 2024+ | Multimodal conversational AI | Unified text, voice and image interaction | Enables more natural, task-oriented conversations that reflect how people communicate |
1960s: The Rise of the Chatbot
Chatbots made their debut in 1966 when a computer scientist at MIT, Joseph Weizenbaum, created Eliza, a chatbot based on a limited, predetermined flow. Eliza could simulate a psychotherapist's conversation through the use of a script, pattern matching and substitution methodology.
Although Eliza could pass a restricted version of the Turing test — a test that determines if a machine can display intelligent behavior indistinguishable from a human being — and fool people into thinking they were talking to another human, it was simply following rules and simulating the conversation with no real level of understanding.
1970s: New Natural Language Understanding
A decade later, Kenneth Mark Colby at the Stanford Artificial Intelligence Laboratory created a new natural language processing program called PARRY. Although it was the first AI program to pass a full Turing test, it was still a rule-based, scripted program.
1990s: Optimized Natural Language Generation
In 1995, Richard Wallace created the Artificial Linguistic Internet Computer Entity (ALICE). It used what was called the Artificial Intelligence Markup Language (AIML), which itself was a derivative of Extensible Markup Language (XML).
Like its predecessors, ALICE still relied on rule-matching input patterns, which highlights the gap between early chatbot design and today’s probabilistic, generative systems.
Related Article: Is This the Year of the Artificial Intelligence Call Center?
The Advancement of Conversational AI
What is conversational AI today? At its core, conversational AI combines NLP, automatic speech recognition (ASR), dialog management and ML. But in its modern form, it is increasingly powered by large language models that can reason across context, dynamically generate responses and adapt to user intent in real time.
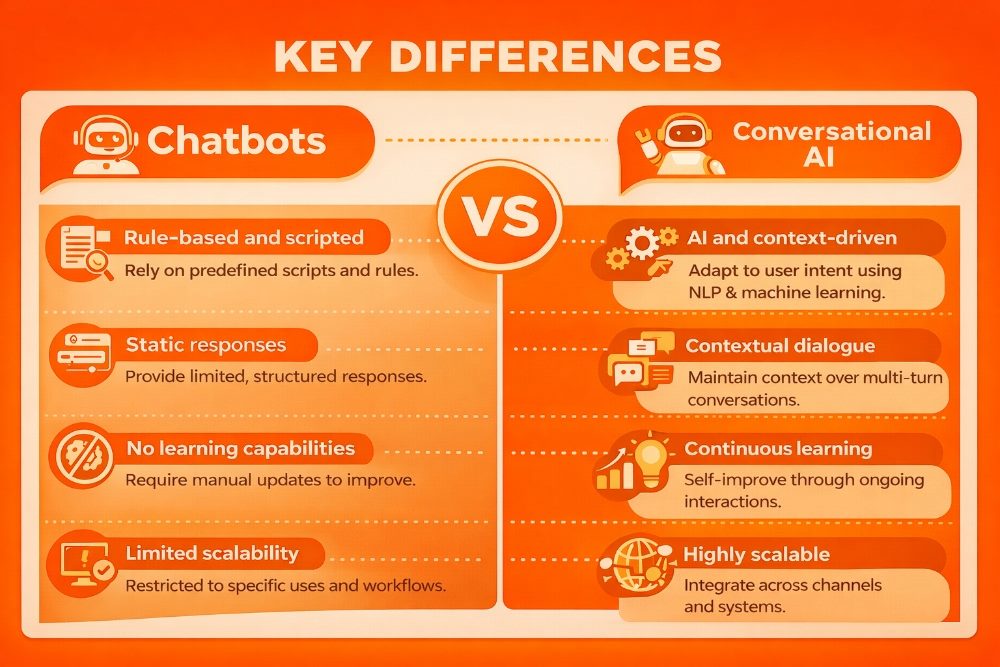
Conversational AI vs. Traditional Chatbots
Many teams still use “chatbot” and “conversational AI” interchangeably, but they aren’t the same. Traditional customer service chatbots typically follow decision trees or rules, while modern conversational AI can interpret intent, maintain context and flex across a wider range of requests.
Key Differences Between Chatbots and Conversational AI
This table compares how legacy bots and modern conversational AI systems behave in real customer and employee interactions.
| Category | Traditional Chatbots | Conversational AI |
|---|---|---|
| How it responds | Chooses from predefined answers | Generates responses based on context and intent |
| Best at | FAQs and simple workflows | Multi-step tasks, nuanced requests and varied phrasing |
| Context handling | Limited memory across turns | Maintains conversational state across multiple turns and channels |
| Failure mode | Dead ends and “I don’t understand” loops | Graceful clarification, retrieval or escalation when confidence is low |
| Operational requirement | Script upkeep and intent mapping | Orchestration, data access, governance and measurement |
Modern conversational AI increasingly operates within a broader conversational AI platform that connects language models, business logic and enterprise data sources. Earlier conversational systems relied heavily on predefined rules and scripted flows. While effective for narrow use cases, they struggled outside of tightly controlled scenarios.
Modern conversational AI, by contrast, uses deep learning to interpret language probabilistically rather than matching keywords to fixed responses. This allows systems to shift topics, maintain conversational context, and respond in ways that more closely resemble human dialogue.
Recent advancements in generative AI, including OpenAI’s GPT models and Google’s Gemini, have accelerated this shift. These models are trained on vast datasets and designed to understand nuance, infer intent and generate natural language responses on the fly. Rather than selecting from prewritten answers, they construct responses based on context, prior exchanges and the broader goals of the interaction.
As organizations scale usage, conversational AI platforms are designed to support multiple channels, use cases and audiences from a shared orchestration layer. This evolution has expanded what conversational AI can do across a wide range of business functions. In conversational AI for customer service, generative AI-powered assistants can handle complex, multi-turn inquiries with more natural and context-aware responses, escalating only the most sensitive or nuanced issues to human agents.
In content creation, businesses are using conversational AI to draft personalized emails, generate marketing copy and assist with documentation. In professional support environments, these systems can uncover insights, generate reports, or help employees compose responses, saving time and improving productivity.
Benefits of Conversational AI for Businesses and Customers
When conversational AI is designed with strong data access and clear guardrails, it can improve both efficiency and experience outcomes:
- Faster resolution for routine needs. Customers get answers quickly without waiting in queues or navigating complex menus.
- Less repetition across channels. Context carries forward, reducing the “start over” frustration that breaks omnichannel experiences.
- More consistent service quality. Approved knowledge and templates reduce variance while still allowing natural responses.
- Scalable personalization. Responses can reflect journey stage, history, and preferences when data use is governed responsibly.
- Better agent and employee support. Assistants summarize, draft, and retrieve information so humans can focus on higher-stakes work.
This shift has accelerated demand for conversational AI solutions that balance automation, accuracy, and human escalation. Compared with traditional rule-based chatbots, these capabilities represent a fundamental shift. Conversational AI is no longer limited to answering predefined questions. It can adapt its responses based on where a customer is in their journey, what they have already shared, and what outcome they are trying to achieve.
“Rule-based or scripted chatbots are best suited for providing an interaction based solely on the most frequently asked questions. An ‘FAQ’ approach can only support very specific keywords being used,” said Eric Carrasquilla, CEO at Vendavo.
“Conversational AI is ingesting the customer feedback and learning in real time that value, which can be applied to the same question at a different point of a client’s journey,” he added.
As a result, conversational AI can quickly resolve routine inquiries such as delivery dates, tracking numbers, or shipping fees, while ensuring more complex or emotionally sensitive interactions are routed to live representatives when appropriate.
“The appropriate nature of timing can contribute to a higher success rate of solving customer problems on the first pass, instead of frustrating them with automated responses,” Carrasquilla said.
Common Use Cases for Conversational AI
Conversational AI shows up across customer experience and internal operations because it can handle high-volume interactions while preserving context and intent. Common use cases include:
Customer Service and Support
Conversational AI can answer routine questions, troubleshoot issues, and route complex situations to agents with conversation history attached. The value is less about automation and more about reducing friction and repetition.
Sales and Commerce
In shopping and sales environments, conversational AI can guide discovery, explain options, and help users complete transactions through natural dialogue. These experiences work best when the system can access product data, inventory, and order status in real time.
Employee Support and IT Help Desks
Internal assistants can support employees by summarizing policies, drafting messages, and helping complete common tasks. When connected to approved knowledge sources, these systems reduce time spent searching and standardize responses.
Accessibility and Voice-Based Experiences
Conversational AI can support voice navigation, speech-to-text, and multimodal assistance for users who benefit from non-visual or non-typing interaction patterns. The experience improves when context carries across devices and sessions.
Multimodal AI: Expanding Conversational Capabilities
One of the most significant shifts in conversational AI is the move toward multimodal systems. Rather than relying on text alone, modern conversational AI models can process and respond across multiple input types, including text, images, and voice, within a single interaction.
Multimodal models such as OpenAI’s ChatGPT, beginning with early multimodal systems like GPT-4o and extending into newer generations, illustrate how conversational AI is evolving beyond text-based exchanges. These systems can interpret images, understand spoken language, and generate responses that combine multiple forms of input and output. The result is a more fluid, task-oriented interaction that more closely mirrors how people communicate in real life.
In practical terms, multimodal conversational AI is already changing how people interact with businesses and digital services. In retail, customers can upload photos to receive product recommendations or ask questions using voice rather than typing. In customer service, multimodal assistants can analyze images alongside text, such as reviewing a photo of a damaged product to help diagnose an issue or guide troubleshooting. In accessibility-focused use cases, these systems can convert speech to text, provide voice-based navigation, or interpret visual information for users with impairments.
Strong conversational AI design focuses on how context, timing, and modality work together to support user intent rather than forcing rigid interaction patterns. What makes multimodal AI especially impactful is not the novelty of multiple inputs, but the way those inputs are combined into a single conversational context. Text, voice, and visual cues are no longer treated as separate channels. Instead, they inform one continuous interaction, allowing conversational AI to respond more accurately and intuitively to user needs.
Multimodal AI represents a shift toward more natural, user-centric conversations. By integrating multiple forms of input and output, conversational AI systems can support richer interactions that are better aligned with how people communicate, solve problems, and make decisions.
Related Article: How AI in Ecommerce Is Getting Talkative
People Trust Conversational AI Solutions
Conversational AI is no longer just a concept; it’s a growing market with real economic weight behind it. According to a recent AI Chatbot Global Market Report, the AI chatbot segment alone was valued at roughly $8.6 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to nearly $29.2 billion by 2029, reflecting a growing demand for automated conversational tools and services.
GenAI adoption data increasingly reflects conversational AI behavior because the primary way people experience LLMs today is through conversational interfaces. While not all generative AI use is conversational in nature, tools such as ChatGPT represent the most widely adopted conversational AI interfaces to date. Although some conversational AI systems still rely on intent-based or scripted approaches, the majority of conversational experiences that customers encounter today are now powered or enhanced by generative AI models.
This growth mirrors how conversational systems are becoming embedded into everyday workflows, from customer service and process automation to internal support and real-time assistance. As usage expands, trust increasingly depends on transparency, reliability, and clear escalation boundaries.
Conversational AI has moved well beyond niche experimentation. A 2025 Pew Research Center survey found that roughly 34% of U.S. adults report having used ChatGPT, about double the rate from 2023, and more than half of adults under 30 say they’ve tried it at least once. This shift reflects how these tools are becoming part of routine digital behavior, whether for information discovery, task assistance, or simple experimentation with AI-powered conversation.
Trust in conversational AI, however, is nuanced. Studies by Forbes Advisor suggest that while many consumers are comfortable engaging with businesses that use AI, trust is closely tied to transparency, usefulness, and the perceived quality of the interaction. Users are more likely to trust conversational AI when it delivers accurate answers quickly and promptly escalates when it cannot.
This pattern extends into the workplace. Research from Oracle and Future Workplace found that employees increasingly rely on AI-powered assistants for guidance, information retrieval, and task support, often interacting with those systems through conversational interfaces. In some cases, workers reported trusting AI tools for unbiased information or scheduling support more than traditional managerial channels, particularly for routine or low-risk decisions.
Beyond practical and professional tasks, conversational AI is also being used in more personal contexts. A recent report from The American Psychological Association revealed that some users turn to conversational systems for emotional support, companionship, or reflective conversation. Platforms such as Microsoft’s Xiaoice, which has engaged hundreds of millions of users over its long lifetime, is indicative of how conversational AI can fulfill social and emotional roles alongside functional ones.
Taken together, these trends suggest that conversational AI is no longer judged solely on whether it can “sound human.” Instead, users evaluate it based on reliability, relevance, and context. Trust is earned through consistent performance and clear boundaries, not simply through conversational fluency.
Challenges and Limitations of Conversational AI
Conversational AI performs best when organizations plan for its constraints. Common limitations include:
- Confidence gaps. If the system can’t verify an answer, it needs a reliable way to clarify, retrieve, or escalate.
- Data and knowledge drift. Outdated policies and stale knowledge bases lead to “confidently wrong” responses.
- Governance overhead. Access control, privacy, and auditability become essential once conversational AI touches real customer data.
- Over-automation risk. When AI is used where empathy or judgment is required, experience quality can degrade fast.
- Measurement confusion. Teams often track containment instead of outcomes like resolution quality, effort reduction, and successful handoffs.
These challenges don’t make conversational AI less valuable, but they do change how teams should evaluate success and where they should keep humans in the loop.
Conversational AI Is Trusted — but Is It Safe?
As conversational AI became more embedded in daily workflows and personal routines, trust shifted from a theoretical concern to a practical one. People increasingly rely on conversational systems to search for information, resolve issues and, in some cases, discuss personal or sensitive topics. That raises an important question: how safe are these interactions?
Like most digital systems, conversational AI is only as safe as the technology and governance behind it. Users are placing trust not just in the interface they interact with, but in the businesses that design, deploy and manage these systems. Evaluating the safety of a conversational AI application requires understanding how it handles data, how conversations are stored or logged, and what safeguards are in place to prevent misuse.
When evaluating a conversational AI application, there are a few baseline indicators of safety. Strong encryption should protect conversations in transit and at rest, particularly for systems operating in regulated environments. Authentication controls help ensure that only authorized users can access sensitive interactions. Clear, accessible privacy policies should explain how conversational data is collected, stored and used, including whether it is retained for training or analytics purposes.
Users also play a role in maintaining safety. Basic security practices, such as using strong passwords, enabling multi-factor authentication and keeping applications up to date, still matter. However, the burden of protecting conversational data increasingly falls on the brands that are deploying these systems, not on the individual users working with complex AI architectures.
Businesses (and People) Rely on Omnichannel Conversational AI
Many early conversational AI implementations struggled because they were deployed as isolated tools rather than integrated systems. Traditional chatbots were often confined to a single channel, usually a website, and designed to resolve isolated interactions. Conversational AI systems are increasingly omnichannel by design, allowing conversations to move fluidly across web chat, mobile apps, voice assistants, messaging platforms, and contact centers without losing context.
Signals That Conversational AI Has Entered the Mainstream
This table highlights adoption and market indicators that show conversational AI has moved from experimentation into everyday use.
| Indicator | Recent Data Point | What It Indicates |
|---|---|---|
| Consumer exposure to conversational AI | 34% of U.S. adults report having used ChatGPT (2025) | Conversational interfaces are now a common entry point for AI use |
| Younger user adoption | More than half of adults under 30 have used ChatGPT | Expectations for conversational, context-aware systems are forming early |
| Conversational AI market growth | AI chatbot market projected to reach nearly $29.2B by 2029 | Businesses are investing heavily in conversational systems as core infrastructure |
| Voice-first conversational usage | Over 87 million smart speakers shipped globally in 2024 | Conversational AI increasingly extends beyond screens into everyday environments |
Users expect to start a conversation in one channel and continue it in another without repeating themselves or losing momentum.
How to Measure Conversational AI Success
Conversational AI performance is often judged by automation rates, but the strongest programs measure whether customers and employees actually achieve their goals with less effort.
- Resolution rate. Did the interaction solve the problem without creating follow-up contacts?
- Effort reduction. Did the system eliminate repetition, channel-switching, or unnecessary steps?
- Escalation quality. When the AI hands off, does the agent receive context, intent, and a clean summary?
- Accuracy under pressure. How does the system perform on edge cases, policy questions, and ambiguous requests?
- Trust signals. Do customers accept the answer, ask for a human, or challenge the response?
These measures align conversational AI to experience outcomes, not just containment.
Smart speakers and voice-enabled assistants have become one of the most common ways people interact with conversational AI outside of traditional screens. According to a recent Statista report, global smart speaker shipments reached more than 87 million units in 2024, and the market is projected to grow to nearly $30 billion by 2029, driven in large part by advances in AI-powered assistants and smart home integration.
As these devices evolve, conversational AI is shifting from simple voice commands to more natural, context-aware interactions. Statista’s smart speaker analysis indicated a shift toward more AI-driven assistants, noting that platforms such as Amazon’s Alexa Plus and Google’s Gemini-powered experiences are expanding smart speakers beyond simple voice commands and deeper into integrated, context-aware interactions across apps, devices, and daily routines.
In enterprise environments, the same pattern is emerging. In contact centers, conversational AI is increasingly used to handle triage, routine resolution, and information retrieval, allowing human agents to focus on higher-complexity or emotionally sensitive interactions.
"The pairing of intelligent conversational journeys with a fine-tuned AI application allows for smarter, smoother choices for customers when they reach out to connect with companies," said Carrasquilla.
Chris Radanovic, director of product marketing at Infobip, told CMSWire that in his experience, using conversational AI applications, customers can connect with brands in the channels they use the most.
“Intelligent virtual concierges and bots instantly greet them, answer their questions and carry out transactions, and if needed connect them to agents with all of the contextual data they’ve collected over the course of the conversation.”
Related Article: AI Cybersecurity: Safeguarding the AI-Driven Customer Experience
Conversational AI Facilitates Hyper-Personalization
Hyper-personalization has become one of the most important differentiators in modern customer experience. Rather than treating each interaction as a standalone event, conversational AI enables businesses to carry context forward across channels, sessions, and touchpoints, allowing interactions to feel continuous instead of repetitive.
“Hyper-personalization combines AI and real-time data to deliver content that is specifically relevant to a customer,” said Radanovic. That expectation now extends beyond marketing into service, support, and ongoing customer engagement.
Radanovic emphasized that consumers increasingly favor conversational AI because it delivers personalized experiences more quickly and conveniently than traditional service models. Customers no longer want to wait on hold, navigate complex phone trees, or click through multiple pages to find relevant information. They expect systems to recognize them and adapt in real time.
According to Radanovic, one of the biggest pain points conversational AI can address is unnecessary repetition.
“A giant source of frustration for consumers is repeating information they’ve already shared, like re-confirming a phone number or having to re-explain a problem to multiple agents,” he explained.
As brands connect conversational AI systems to customer data sources, including conversation history, stated preferences, and prior interactions, those systems can maintain continuity across engagements. The result is a more fluid, personalized experience that feels less like interacting with a system and more like continuing an ongoing conversation.
Conversational AI Is Part of Our Daily Lives
Modern conversational systems now support fluid, context-aware interactions across channels, devices, and use cases. From customer service and virtual assistants to professional support and reflective conversation, conversational AI has expanded into areas that once required human mediation. These systems can guide shoppers, assist employees, translate languages in real time, and help people navigate complex information without forcing them to adapt to rigid interfaces.
What has changed most is not just capability, but expectation. Conversational AI is no longer something users consciously “try.” It is increasingly embedded into how people search, ask questions, complete tasks, and interact with businesses. Conversations move across text, voice, apps, and devices with continuity, and users now expect systems to remember context rather than restart interactions from scratch.
For businesses, conversational AI has become a foundational layer for customer engagement, enabling scalable personalization and insight across channels. For individuals, it has become a practical tool for organizing daily life, accessing information, and reducing friction in routine tasks.
Conversational AI is no longer emerging. It is already woven into how people work, communicate, and make decisions. As the technology continues to mature, its role will feel less like interacting with a system and more like continuing a conversation that already understands where you are coming from.