Your next collaborator isn't a sci-fi robot; it's a highly efficient crew of AI agents, already capable of moving beyond mere conversation to commit code, close IT support tickets and streamline complex approval workflows — all while keeping you in the loop for final approval.
Why It Matters for HR Leaders
The implications for Human Resources departments are particularly profound. HR professionals — and knowledge workers more broadly — can get bogged down by repetitive tasks and fragmented systems. Employees reportedly spend nearly 20% of their workweek — roughly one full day — just searching for information needed to do their jobs effectively. These poor experiences not only drain productivity but also delay decision-making and diminishes employee satisfaction.
This is where vendors see AI agent crews, powered by advanced Large Action Models (LAMs), stepping in. These AI teams can eliminate such inefficiencies by handling critical processes like new employee onboarding, responding to repetitive HR queries, and managing IT and approval workflows. By automating these functions, HR teams can dedicate their valuable time and expertise to more strategic, human-centric endeavors such as employee coaching, cultivating a strong company culture and enhancing the overall employee experience.
IBM's Blueprint: HR as “Client Zero” for Agentic AI
IBM isn’t only selling AI agents, it is using the technology internally. IBM Chief Human Resources Officer, Nickle LaMoreaux, champions the idea of HR as “client zero” for generative AI adoption. "We believe HR should lead by example ... so HR professionals can put that time into higher-value efforts,” she explained in an interview with Berkeley Haas.
The results from IBM’s "AskHR" initiative have demonstrated tangible benefits:
- 94% of HR inquiries are now resolved automatically.
- This translates to $5 million saved annually.
- 50,000 hours have been reclaimed for HR staff to focus on strategic work.
- Employee satisfaction has soared, reflected in an Employee Net Promoter Score (NPS) of +74.
While IBM’s recent reduction in HR headcount — prompted by AI agent adoption — has been widely discussed in our field, CEO Arvind Krishna framed it as part of a broader reinvestment strategy: "While we’ve leveraged AI and automation in enterprise workflows, our overall employment has actually gone up. It allows us to reinvest in growth areas, placing a premium on adaptability and continuous reskilling."
The A.C.E.S. Framework: Your Playbook for Agentic AI
To navigate this new landscape and implement AI agent crews effectively and responsibly, I've developed my proprietary A.C.E.S. framework. This playbook is designed to guide organizations from initial concept to scalable impact.
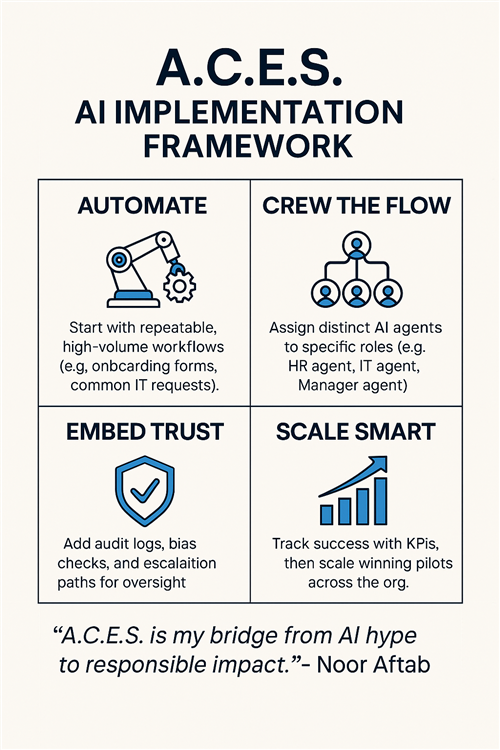
A.C.E.S. is my bridge from AI hype to responsible impact.
- Noor Aftab
Large Action Models (LAMs): From Chatbots to “Do-Bots”
LAMs are the engine driving these intelligent agent crews. While traditional chatbots primarily retrieve and relay information, LAMs are designed to do. They are trained not just on text, but on actions (such as specific Workday API calls), entire workflows and underlying business logic.
Key capabilities of LAMs include:
| Goal Inference | They can learn from historical data, like past support tickets, to understand the desired outcome of a task. |
| Contextual Adaptation | LAMs can dynamically reroute tasks or escalate to human counterparts based on the complexity or novelty of a situation. |
| Auditable Execution | Every action taken by a LAM is logged, providing audit trails for compliance with regulations like GDPR, SOX and the EU AI Act. |
Decision Matrix: Pick Your AI Agent Stack
Choosing the right technology stack is crucial for successfully deploying AI agent crews. The landscape offers various frameworks, each suited to different needs and organizational contexts.
Framework | Best For | Integrations | Governance & Compliance | Code Complexity |
| IBM watsonx Orchestrate | Regulated industries, HR/IT | 80+ apps (Workday, SAP) | SOC2, HIPAA, EU AI Ready | Low (Visual) |
| OpenAI Agents SDK | Developer-led, custom workflows | Slack, Python SDK | Schema validation, logs | Medium (Python) |
| NVIDIA AI-Q | ML/data ops, GPU-intensive analytics | GPU workflows | ML traceability | High (Cluster) |
| CrewAI (Open Source) | Startups, rapid prototyping, DIY solutions | 700+ via LangChain | Customizable, community-driven | Low (YAML/Python) |
💡Tip: The AI agent space is dynamic — new enterprise offerings from providers like Amazon and SAP continue to emerge, giving organizations even more choice and flexibility across industries.
Try This: Conceptualizing Your First AI Agent Crew
Getting started with AI agent crews can be more accessible than you might think and does not necessarily demand deep coding expertise from the outset. The core idea involves defining roles, tasks, and how they interact. Conceptually, setting up a simple onboarding crew involves these kinds of steps:
Step 1: Define Agent Roles & Goals
- HR Agent: Goal is to ensure new hire complete on boarding paperwork and are informed of company policies.
- IT Agent: Goal is to provision necessary IT accounts, software licenses, and hardware for these new hires.
- Manager Agent or Human Manager: Goal is to review and approve on-boarding steps and resource allocation.
Step 2: Assign Specific Tasks
- HR Agent: Task to guide new hire through paperwork completion and collect all signed documents.
- IT Agent: Task to set up the new hire’s IT accounts, install required software, and confirm hardware readiness.
- Manager Agent: A task to verify completion of HR and IT onboarding steps and provide final allocation.
Step 3: Orchestrate the Workflow
- Determine workflow sequence: (Sequential in this case) From HR Agent to IT Agent to Manager Agent.
- Define hand offs and triggers.
Step 4: Incorporate Oversight & Metrics
- Assign monitoring responsibility: Designate who (e.g., Oversight Agent or Manager) will track overall progress.
- Setup Dashboards or reporting tools: Use visual tools or reports to track task completion, timelines and blockers.
- Define Success Metrics: Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) like time-to-onboard, error rates and completion rates to measure effectiveness.
✏️ Note: Remember that each agent handles multiple detailed sub-tasks. In our case these will be benefits enrollment, tax forms and compliance training for HR Agent; Email setup, software access, hardware delivery and security permissions for IT agent; and Team integration, approvals and setting expectations for Manager Agent.
Platforms and frameworks are emerging that allow business users or citizen developers to configure this logic, often visually or with minimal, simplified scripting. This approach makes the power of AI agent crews accessible beyond traditional engineering teams, empowering HR and operations leaders to design and implement their own automated workflows.
How AI Agents Are Driving Impact
Across industries, AI agents are no longer experimental, they’re driving measurable change.
- Banking: Bank of America’s Erica virtual assistant has handled over one billion customer interactions, streamlining service and freeing human teams for higher-value work.
- Telecommunications: Vodafone’s AI agent cut conversational testing timelines from over six hours to under a minute, accelerating customer experience innovation.
- Retail: H&M’s virtual shopping assistant boosted online conversions by over 25% through personalized recommendations, enhancing both sales and customer satisfaction.
These examples show that even while multi-agent coordination is still evolving, focused, single-agent deployments are already reshaping business operations today — offering a glimpse of the broader transformation ahead.
A Note on the Road Ahead: While LAMs are still an evolving technology, these early wins highlight their promise. For HR leaders, the opportunity lies in thoughtful adoption, ensuring automation amplifies, rather than replaces, the human strengths that drive organizational success.
The Future is Crewed: Embrace Intelligent Automation
The era of AI agent crews is dawning, moving artificial intelligence from a passive assistant to an active participant in our daily work. For leaders in HR, IT and across all business functions, these AI teammates offer an unprecedented opportunity to automate complex processes, enhance efficiency and free up human talent for the strategic, creative and empathetic work that truly drives value.
By understanding the capabilities of LAMs, using frameworks like A.C.E.S. and starting with targeted pilot projects, organizations can begin to re-engineer teamwork for a more productive and intelligent future. Your next most effective teammate might just be an AI crew.
Editor's Note: Catch up on more news in the AI agent space:
- ServiceNow and Salesforce Fight to Be the Center of AI Agent Operations — Salesforce and ServiceNow move into each other’s domains, but their eyes are on a much bigger prize.
- How SAS Is Developing Responsible Agentic AI — It's not enough for AI agents to be autonomous. They also have to be accountable. SAS's Viya platform is trying to make that happen.
- How Agentic AI Will Change the Workplace: An Insider View — Employees of some of the major tech vendors in the agentic AI space discuss opportunities and challenges associated with the technology.
Learn how you can join our contributor community.
