Key Takeaways: UK Investigates Google AI Overviews
- The UK's Competition and Markets Authority (CMA) is investigating Google AI Overviews for potentially stifling competition and reducing publisher traffic.
- Publishers report significant traffic losses from AI-generated summaries that answer user queries without requiring clicks to original websites.
- Zero-click searches are increasing as Google's AI Overviews provide direct answers at the top of search results pages.
- Proposed remedies include mandatory attribution, traffic-sharing requirements, and limits on Google's self-preferencing in AI answers.
Google AI Overviews is facing a UK investigation after its rollout. The AI summaries have triggered immediate backlash, prompting regulators, publishers and privacy advocates to sound the alarm over the search monopoly and what some are calling a “reckless” disruption of the information ecosystem.
Critics argue that Google’s new AI Overviews — known during testing as the Search Generative Experience (SGE) — summarized answers generated by its Gemini model — not only sideline independent publishers but introduce factual errors. Now, with both the UK Office of Communications (Ofcom) and the UK’s Competition and Markets Authority (CMA) watching closely, pressure is mounting to investigate whether Google’s AI search enhancements risk cementing its dominance in a way that stifles competition, transparency and digital pluralism — the principle that no single platform should dominate how information is accessed or interpreted online.
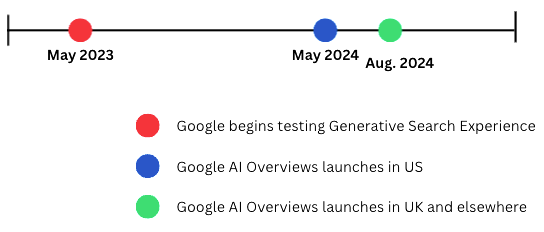
Table of Contents
- UK Competition Authority Takes Action Against Google's AI Search
- How Google AI Overviews Reduce Website Traffic and Revenue
- UK Regulators Push for Digital Pluralism in AI Search
- Why the UK's Google Investigation Could Change AI Search Globally
- The Future of AI-Powered Search: Competition vs. Innovation
UK Competition Authority Takes Action Against Google's AI Search
The UK’s CMA has turned its attention to Google’s growing dominance in generative search, launching an investigation that could reshape how generative AI is used in search results. At the heart of the probe are concerns that Google’s AI Overviews may unfairly divert traffic from publishers and rivals, tightening the company’s grip on digital discovery. Critics argue that these AI‑generated answers risk creating a closed ecosystem where Google both sources and owns the user journey, raising urgent antitrust questions.
This action isn’t happening in a vacuum. It reflects a broader European push to safeguard digital pluralism and curb the power of platforms that might otherwise control the flow of information. With regulators across the EU watching closely, the CMA’s investigation signals that the rules of engagement for AI‑enhanced search may soon be rewritten.
Publisher Complaints Spark Google AI Overviews Investigation
Google’s AI Overviews has expanded into UK search results, presenting AI‑generated summaries at the very top of search engine results pages (SERPs). Instead of clicking through to multiple sources, users are now offered synthesized answers on the spot. While Google argues this improves efficiency and user satisfaction, many publishers and advertisers see a different picture: one where their hard‑earned traffic is siphoned away before users ever reach their sites.
Industry Reactions to CMA Investigation
While the investigation signals a serious intent to scrutinize Google’s practices, many observers have noted that large tech platforms often adapt with minimal disruption despite tough-sounding inquiries.
"While the UK and Europe are willing to be bullish with American technology companies on privacy and data laws, the start of this investigation is unlikely to spark any serious consequences for Google or the search ecosystem," Sam Marlow, senior SEO strategist at POLARIS, explained, adding that even strong recommendations are unlikely to force significant product changes given Google’s entrenched position in search.
What Triggered the Formal Investigation
Complaints to the CMA began surfacing soon after the rollout. News organizations and independent creators have raised alarms about content being summarized without sufficient attribution, while advertisers and rival search providers argue that Google’s placement of AI Overviews entrenches its dominance by keeping users inside its own ecosystem. Some critics have also questioned whether the algorithm behind these AI summaries favors certain sources or viewpoints, fueling concerns over AI bias and lack of transparency.
These grievances echo similar debates across Europe. Under the EU’s Digital Markets Act (DMA), regulators are already scrutinizing how gatekeepers like Google wield their AI capabilities in search and advertising.
Related Article: Google’s AI Mode Signals a New Era in Search
How Google AI Overviews Reduce Website Traffic and Revenue
With Google's AI overviews providing searchers with answers without having to navigate anywhere else, the natural result is reduced clicks to individual websites and eroded organic traffic that fuels publishers’ ad revenue. Many publishers argue that the system effectively captures and repackages their work without meaningful credit or compensation, while advertisers worry that fewer site visits mean fewer opportunities for engagement.
The Zero-Click Search Problem
"There’s no question that AI Overviews have accelerated the rise of zero-click search… fewer clicks, less traffic and often fewer conversions for content creators," said Charlie Marchant, CEO of Exposure Ninja. While AI overviews optimize the user experience, he noted, they simultaneously diminish the referral traffic that publishers have long relied on.
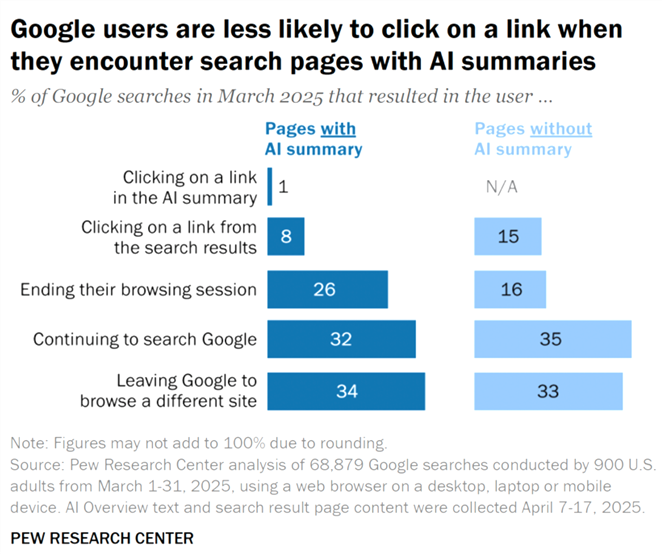
Recent data shows that when Google users encounter an AI summary, only 8% click on a traditional search result link. Of those that encounter AI summaries during their searches, only 1% clicked on a link within the summary.
Attribution and Copyright Concerns
Critics have also taken aim at the opaque nature of the AI’s training data and ranking logic. Because the models are trained on vast swaths of web content, it’s unclear how much of the output is derived from copyrighted or sensitive material. That uncertainty has already sparked legal action elsewhere — Reddit, for example, recently sued Anthropic over claims that its AI models reproduced Reddit content without permission.
Early tests of AI Overviews have also surfaced factual errors and odd hallucinations — mistakes that risk spreading misinformation at scale. Combined with Google’s unrivaled reach, the feature consolidates even more control inside a single ecosystem, which is precisely why it has become the latest flashpoint in the debate over competition and accountability in AI-driven search.
Unexpected Benefits for Lower-Ranked Content
Some specialists have noted that these AI summaries can occasionally elevate content that might not have surfaced under traditional rankings.
"[AI Overviews] often surface content from beyond the first page, giving lower-ranked pages a shot at visibility they’d never get through traditional SEO," said Marchant. "While the click may be gone, the brand impression isn’t."
UK Regulators Push for Digital Pluralism in AI Search
“Competition and innovation must thrive side by side, or consumers lose out on choice and quality.”
- Dr. Andrea Coscelli
[Former Chief Executive, Competition and Markets Authority (CMA)
CMA's Goals: Competition and Transparency
The UK’s Competition and Markets Authority (CMA) has made it clear that its investigation into Google’s AI-enhanced search isn’t just about one product — it’s about the shape of the internet ecosystem itself. The CMA’s stated goals are to preserve competition, demand transparency in how AI summaries are generated and protect consumer choice so that users aren’t quietly funneled into a single platform’s preferred answers.
Central to this effort is the idea of digital pluralism. When one dominant platform’s AI layer becomes the gatekeeper to information, it risks shrinking that diversity by siphoning traffic away from publishers and smaller rivals. Dr. Andrea Coscelli, a former CMA chief executive, summarized the agency’s broader stance in earlier remarks on digital markets: “Competition and innovation must thrive side by side, or consumers lose out on choice and quality.”
Proposed Remedies and Solutions
Industry voices have stressed that oversight must be carefully structured so that it protects diversity in search results without discouraging technological progress.
"Innovation in AI search brings convenience and progress, while it can cause concentration of power and sideline independent voices," said Fergal Glynn, chief marketing officer and AI security advocate at Mindgard. "The best approach is to set clear rules that protect competition and require transparency on how these AI summaries are created and sourced." He suggested that regulators create policies that safeguard fair access and attribution without stifling innovation.
Potential remedies are already on the table. Regulators could mandate interoperability, ensuring that AI-powered search features work more openly with third-party services. They may impose limits on self-preferencing, preventing Google from favoring its own properties in AI answers. Clearer attribution rules are also being discussed, requiring that AI summaries visibly credit and link back to original sources.
For the CMA, the investigation isn’t simply about policing one tech giant — it’s about setting guardrails that keep the internet’s information ecosystem vibrant, competitive and trustworthy.
Related Article: Anthropic Accused of Massive Data Theft in Reddit Lawsuit
Why the UK's Google Investigation Could Change AI Search Globally
The CMA’s investigation isn’t happening in isolation — it’s part of a growing international pushback against unchecked dominance in AI-driven search. Across the EU, enforcement of the Digital Markets Act is already putting tech giants under stricter scrutiny, while regulators in Canada and the United States are openly questioning how generative search reshapes competition and access to information. Together, these moves suggest that the UK’s action could mark a tipping point, setting precedents that shape new global norms for AI in search.
Impact on Alternative Search Engines
For smaller challengers — platforms such as Brave or Perplexity AI — the outcome is critical. They have have built their appeal on transparency, privacy or curated experiences, and they’re watching closely to see whether regulators will level the playing field. A shift toward clearer attribution and fairer traffic distribution could give them space to compete with dominant players.
Potential Consequences for Google
For Google, the risks are significant. Beyond potential regulatory fragmentation — having to meet different compliance standards in each jurisdiction — the investigation could slow product rollouts or force feature redesigns to avoid penalties. And with generative search already under scrutiny for factual errors, (referred to as hallucinations) and opaque data practices, any regulatory action also carries the threat of reputational damage at a time when trust is central to user adoption.
The Broader Web Economy at Risk
In short, the UK’s case could become more than a local skirmish. It may shape how AI-powered search evolves, and how every market, from Europe to North America, defines the balance between innovation and fair competition.
The Future of AI-Powered Search: Competition vs. Innovation
Whether this inquiry becomes a catalyst for global standards or just another headline will depend on how regulators, tech leaders and publishers navigate the balance between progress and pluralism in the months ahead.
