Prompt engineering is a sought-after skill in the age of AI, shaping everything from chatbots and copilots to content creation and enterprise workflow automation.
The ability to design clear, effective AI prompts is critical not just for coaxing better answers from large language models (LLMs), but for avoiding costly mistakes and unlocking real return on investment.
Table of Contents
- What Is Prompt Engineering?
- Common Questions About Prompt Engineering
- Why Is Prompt Engineering Important?
- What Does a Good Prompt Look Like?
- Prompting By Model: What's the Difference?
- 6 Types of Prompting
- 5 Prompt Engineering Best Practices
- Prompt Engineering Tools
- What's Next? Prompt Engineering Outlook
What Is Prompt Engineering?
Prompt engineering is the practice of drafting and refining instructions given to AI systems — especially LLMs — to achieve more accurate, relevant and useful results. Instead of just asking a question, you structure the input (using formatting, examples, context, constraints, step-by-step guidance) to steer the model toward the desired output.
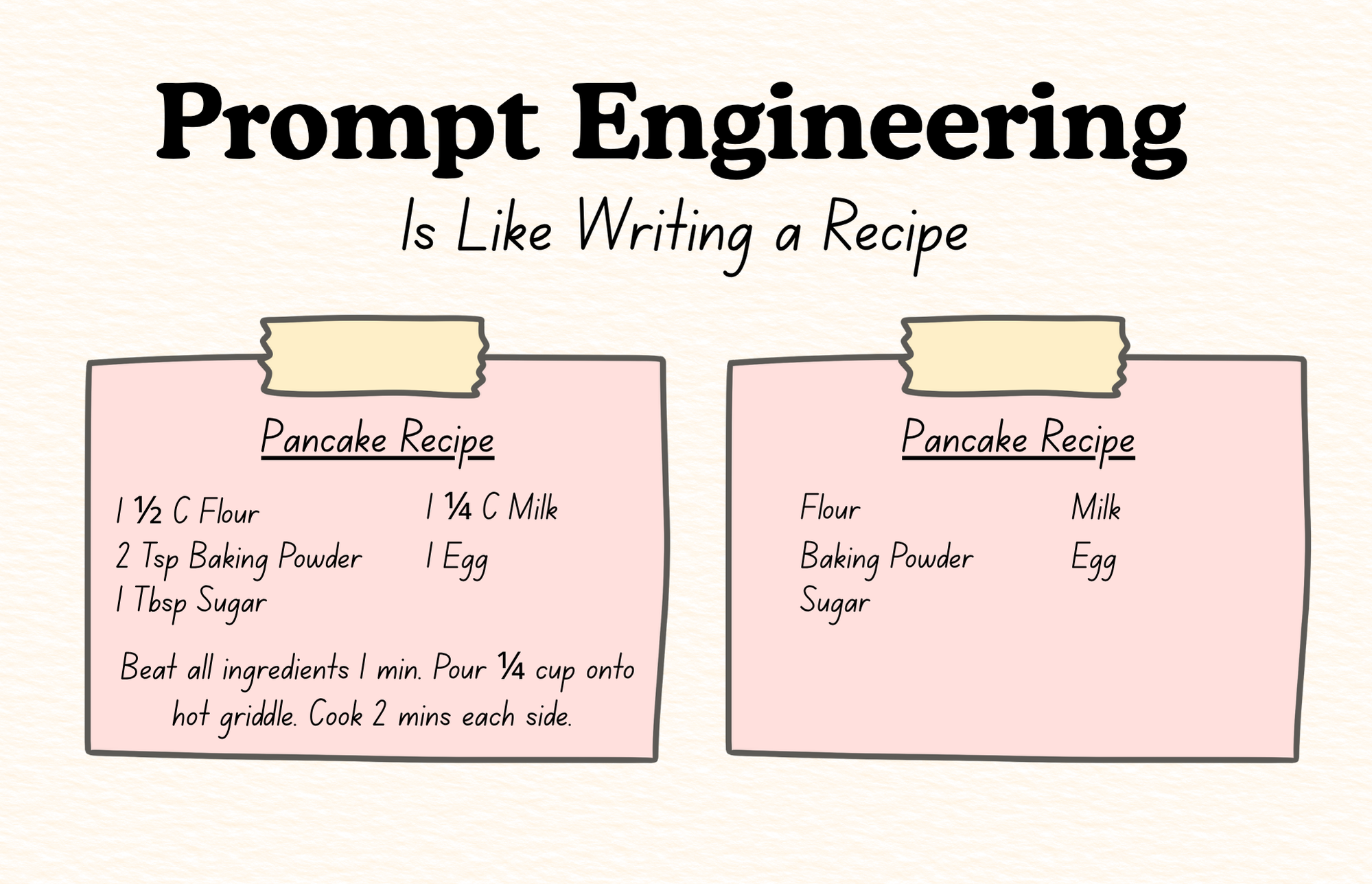
Think of prompt engineering like writing down a sacred family recipe. You wouldn't just write down a list of foods. Instead, you'd include specific amounts for each ingredient and instructions on how to combine them. The more information you include, the better the outcome.
In short: it’s the skill of telling the model exactly what you need, in a way the model understands, so the output meets your goals.
Related Article: CTO’s Guide to Strategic AI Prompting: 20+ Prompts to Master Today
Common Questions About Prompt Engineering
Yes. Learning how to craft good prompts makes AI more reliable and useful. Good prompts reduce hallucinations, improve accuracy and generate outputs you can actually use, saving time and money.
Prompt engineering is a gateway skill to more advanced AI work, like:
- AI automation
- AI agent design
- Workflow orchestration
- Fine-tuning and model evaluation
Demand for prompt engineers has dropped 80%-90% since LLMs first came out in 2022. Today, many companies believe prompt engineering should be a skill that nearly all employees have — similar to being good at searching Google.
Why Is Prompt Engineering Important?
The stakes for getting prompts right have never been higher. In business settings, prompt engineering can mean the difference between a chatbot that delights customers and one that damages trust, or between automated processes that drive productivity and those that create errors and compliance risks.
AI can only act as a perfect assistant if you provide it with a clear structure and context in prompts, said Fergal Glynn, AI security advocate and CMO at Mindgard. "By mastering prompt engineering, one can turn vague requests into specific instructions that AI can reliably follow."
Good prompt engineering:
- Reduces hallucinations
- Improves consistency and factual accuracy
- Aligns the model’s response with a specific role, tone, format or task
- Helps the AI reason through complex problems rather than guess
Prompt Engineering's Impact on AI Output Quality
| Prompt Type | Example | Output Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Vague Prompt | "Summarize this article." | Inconsistent; May include irrelevant info |
| Clear Prompt | "Summarize the key findings in this article in three bullet points; exclude background." | Focused, relevant, easy to use |
| Persona Prompt | "Act as a compliance officer and highlight any regulatory risks in this text." | Contextual, tailored to use case |
| Chain-of-Thought Prompt | "Summarize the key findings in this article in three bullet points; exclude background. Show your reasoning step-by-step as to why you choose these three key insights." | Transparent, logical, reduces errors |
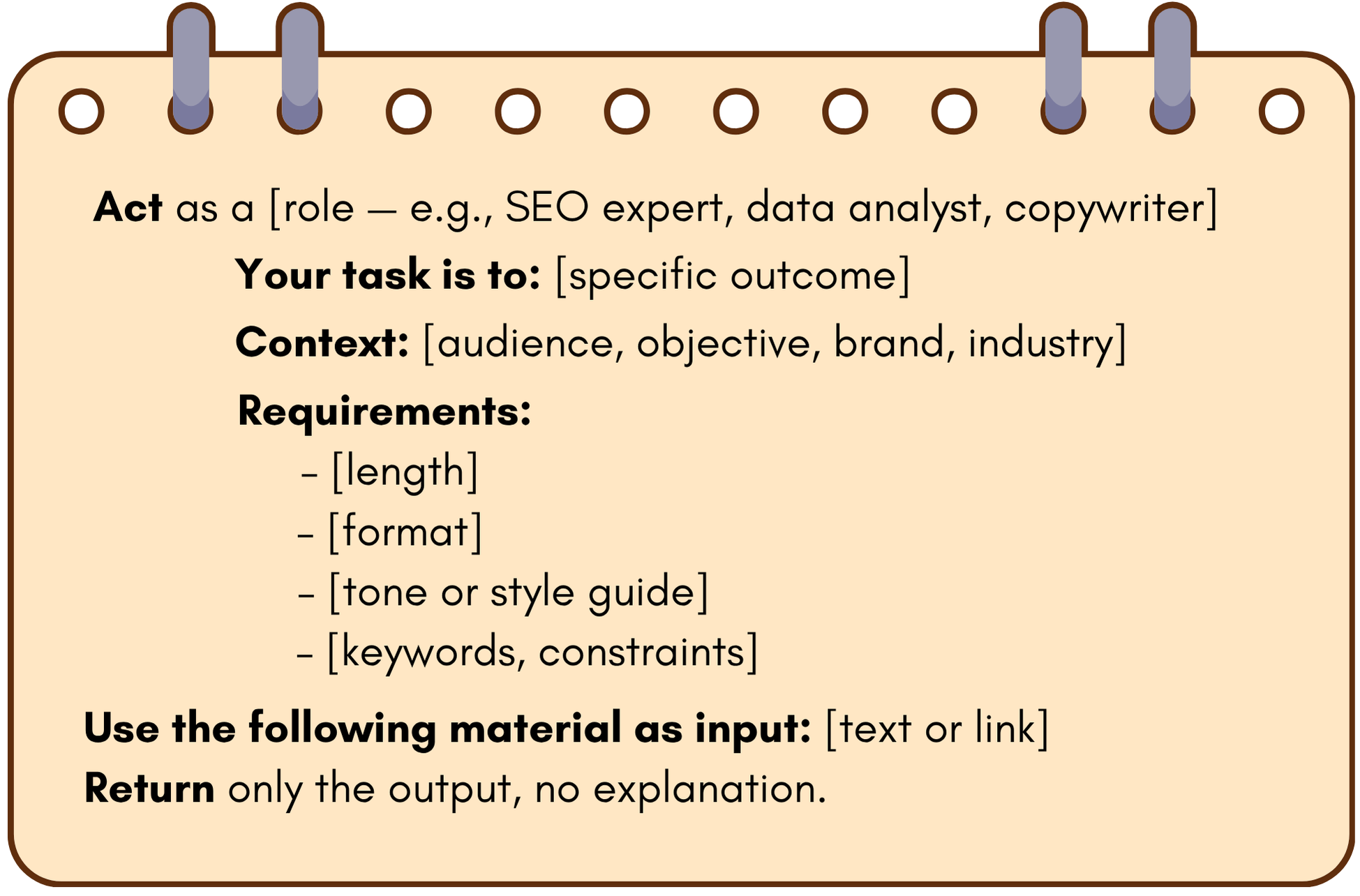
What Does a Good Prompt Look Like?
The biggest misconception with prompting is that you treat it like Google queries, said Naz Avo, AI integration consultant at Hindcast Labs. "What [organizations] don't realize is that LLMs aren’t mind readers — they mirror your prompt."
A good prompt will include:
- The task
- The context
- The constraints or requirements
- Input material (images, research, text)
- An example (powerful but optional)
Prompt Engineering Formula
Prompting By Model: What's the Difference?
Prompt engineering also varies depending on what you’re asking the AI to do — and which kind of AI model you’re working with:
| AI Model | Best Way to Prompt | Prompt Example |
|---|---|---|
| Large Language Models | Prompts must specify tone, format, level of detail and sometimes even persona. | “Act as a customer service agent…” |
| Image Generation Models | The best prompts describe not just the subject but style, color, lighting, mood and composition. | “A photo-realistic image of a golden retriever puppy sitting in a field of sunflowers at sunset, soft lighting." |
| Code Generation Models | Effective prompts outline the language, constraints and expected behavior. | “Write a Python function that takes a list of numbers and returns only the even numbers." |
| Multimodal Models | Here, prompts might combine text, images or even audio cues, requiring clarity in how you blend modalities and what the desired outcome is. | "Transcribe the following audio clip: [audio]" |
In every case, the key is precision: The clearer and more intentional your prompt, the more predictable and useful the AI’s response.
6 Types of Prompting
Prompt engineering has evolved into a nuanced discipline, with practitioners borrowing tactics from programming, copywriting and even psychology to get the best results. At the foundation are six distinct AI prompting styles or strategies.
1. Zero-Shot Prompting
This style of prompt engineering gives the AI model no examples — just the task itself — testing how well it can generalize from the instruction alone.
Example
Explain neural networks in simple terms a 10-year-old could understand.
2. Few-Shot Prompting
Few-shot prompting includes a handful of concrete examples within the prompt to set clear expectations for the output, often leading to more accurate or stylistically consistent responses.
Example
Create headlines that turn complex AI topics into simple, punchy statements. Here are some examples:
Example 1:
Topic: AI Chip Shortages
Headline: Why AI Chips Are the New Oil — And Everyone's Running Out
Example 2:
Topic: Model Collapse
Headline: What Happens When AI Starts Learning From Itself?
Example 3:
Topic: Deepfake scams
Headline: Your Boss Might Not Be Your Boss: Deepfakes Exposed
3. Chain-of-Thought Prompting
With Chain-of-Thought prompting, the input guides the model step-by-step through a reasoning process, helping surface its logic and reduce errors, especially on complex or multi-part questions.
Example
Our website is getting traffic but very few newsletter signups.
List three possible reasons why this might be happening, and for each one, walk through your reasoning step by step before giving a recommendation.
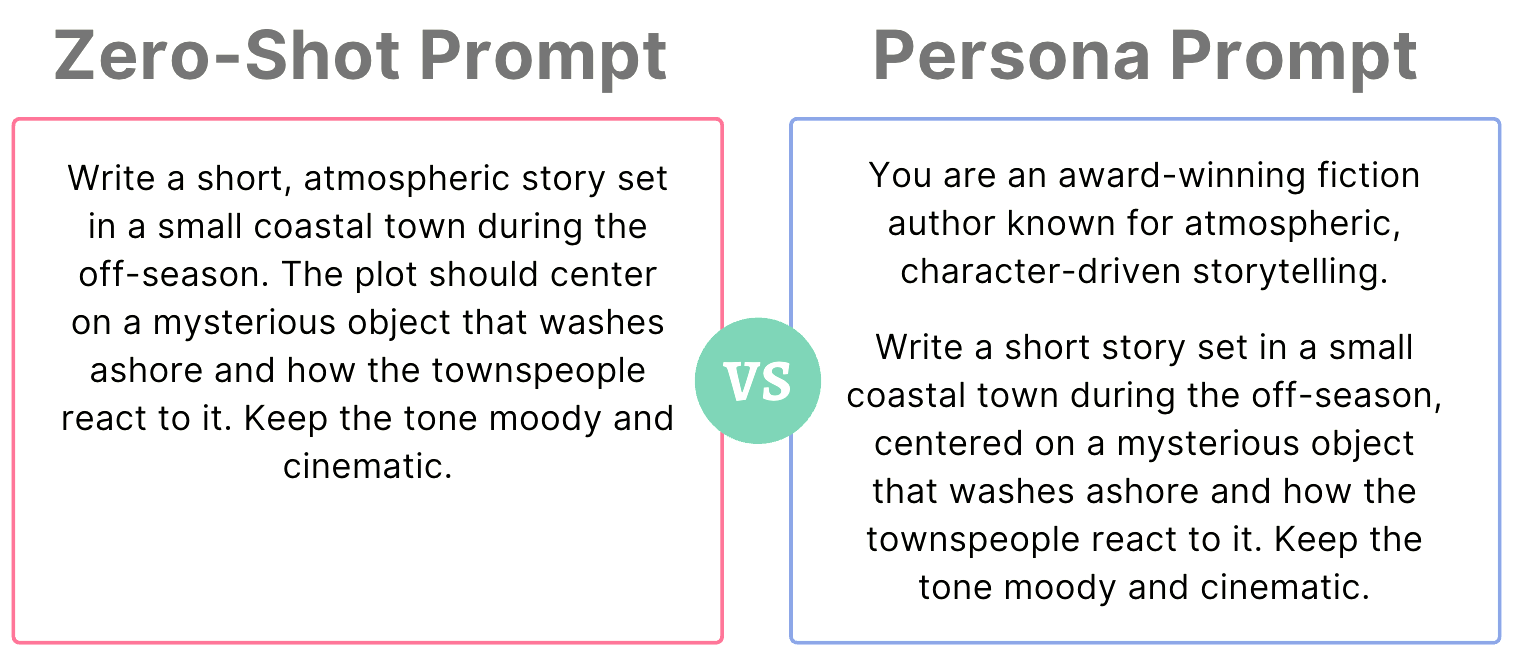
4. Persona Prompting
Persona prompting adds another dimension to prompt engineering, asking the model to “act as” a specific persona — act as a customer service agent, expert analyst, skeptical editor — to shape the tone and substance of the output.
Example
Act as a seasoned travel guide who specializes in affordable, culturally rich itineraries. Create a five-day plan for Lisbon that avoids tourist traps and highlights local experiences.
5. Tree-of-Thought Prompting
Tree-of-thought prompting helps AI reason through problems by exploring multiple possible solution paths instead of generating a single, linear answer. Like branching decisions in a flowchart, the model evaluates different “thought branches,” compares their merits and prunes weak paths as it goes.
Example
I want you to use a tree of thought approach.
For the following problem, generate two different reasoning paths, each exploring a different approach.
Then compare the paths, evaluate which one leads to the most reliable conclusion and give me a final answer.
Problem:
A café wants to increase weekday foot traffic between 2:00PM and 5:00PM. Provide a strategy using the tree-of-thought method.
6. Prompt Chaining
With chain-of-thought prompting, you guide the model through multiple reasoning steps within a single prompt. Prompt chaining is similar, but breaks the steps down into a sequence of smaller prompts, using the output of one step as the input to the next. Instead of asking the model to solve everything at once, you guide it through a structured workflow — generate ideas, filter them, refine one, format it and evaluate the result.
Example
Prompt 1:
Summarize the top five challenges a new organic energy drink brand faces when entering a crowded market.
This generates the root understanding. You now take the output from Prompt 1 and branch in different directions.
Prompt 2A:
Using these challenges, create two distinct brand messaging directions that position our drink uniquely.
Prompt 2B:
Using these challenges, map out how our top four competitors address them and where gaps exist that we can exploit.
Each branch explores a different domain.
Prompt 3A:
Take Messaging Direction #2 from your previous response and write a sample homepage headline and subhead.
Prompt 3B:
Based on the competitor gaps you identified, generate a differentiated value proposition for our product.
Each branch develops on its own “sub-tree.” Now it's time to merge the branches back into one synthesized plan.
Prompt 4:
Combine the strongest insights from x outputs into a single six-point go-to-market plan for the new energy drink.
Related Article: 14 Top Prompt Engineering Certifications
5 Prompt Engineering Best Practices

1. Be Clear
"If you are a team leader or just a beginner in generative AI, the best advice is to make it simple. Do not focus on complex scenarios with several roles in mind. Focus on clarity and structure, define the best practices, and how your AI should interact for the best performance."
2. Manage the Details
Effective prompt engineering means managing the details: specifying the desired output format, controlling the length, setting constraints and fine-tuning tone.
For example, you might direct a language model to “Summarize this in three sentences, using neutral language and include a key takeaway at the end.”
Each layer of specificity closes the gap between intent and outcome, turning probabilistic AI behavior (something that is based on, influenced by or involving the likelihood or probability of different outcomes, rather than certainty) into something far more predictable and usable.
3. Continuously Refine
The process rarely ends with the first draft. Effective prompt engineers iterate relentlessly, testing and refining prompts in response to both model performance and human feedback.
Prompt versioning — tracking how small changes affect results — helps teams develop internal libraries of proven prompts for common tasks. In high-stakes settings, this cycle of experimentation, measurement and improvement is essential for reliability and scale.
4. Choose the Right Prompt Style
Modern prompt engineering is about blending intuition and strategy, not just technical knowledge. The best practitioners know how to pick the right prompt style and adjust for model limitations or business needs.
"A prompt engineer can be the person fine-tuning a single system prompt or the one designing entire workflows where prompts pull in live data from databases or outside platforms," said Zeel Jadia, CEO and CTO at ReachifyAI. "Out of this, a whole toolbox of strategies has emerged, from Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) to Chain-of-Thought prompting and beyond."
5. Share What You Learn
"Encourage teams to share learning with each other because improvements spread quickly," noted Glynn. Document (and share) what prompts work best for you and for which use cases.
Ultimately, prompt engineering best practices are less about technical wizardry and more about clarity, patience and a willingness to treat every prompt as a living experiment — one that can always be tuned for better results.
Prompt Engineering Tools
A growing range of specialized tools has emerged to help teams manage, refine and scale their AI prompting efforts.
- Prompt Management Platforms: Platforms like PromptLayer and Promptist help you catalog, version, share, track and govern prompts across teams and projects.
NoRedInk built prompt versioning that lets 6 teachers control AI grading 1M+ essays. None can code.
— PromptLayer (@promptlayer) August 7, 2025
System handles instant rollbacks, A/B testing, and performance tracking through PromptLayer. 50+ updates ship weekly with 99.9% uptime.
Enterprise-grade AI, teacher-operated: pic.twitter.com/cA3TFWYZvM
- Prompt Testing, Evaluation & Analytics Platforms: These tools help organizations experiment with prompt variants, measure output quality (accuracy, consistency, cost, latency), compare models and track prompt performance over time.
- Prompt Workflow Frameworks: These frameworks or libraries assist when building systems that use prompts as part of broader workflows — chaining prompts, combining with retrieval, external tools, multimodal inputs, managing logic beyond a single prompt.
- Prompt Libraries and Marketplaces: These repositories allow you to access pre-built prompt templates (industry-specific, model-specific), share them across teams or even monetize them.
- Interactive Playgrounds and Prototyping Tools: These are lighter-weight, often UI-based tools for exploring prompts, testing them with different models and quickly iterating by hand (often before operationalizing).
- Custom GPTs in ChatGPT: Custom GPTs bring added value and make prompt engineering less complicated, according to Victor Horlenko, head of AI innovations at Devart. You can pre-design the model to craft prompts according to brand guidelines and share it with everyone in your organization.
Related Article: The AI Accuracy Crisis: How Unreliable LLMs Are Holding Companies Back
What's Next? Prompt Engineering Outlook
With all the fancy new models on the market and context-aware features, many people think prompt engineering is no longer important. In reality, it's the opposite, said Horlenko.
"More 'advanced' models often require clear and more guided input to show the best performance in results. Looking at current trends, prompt engineering will not disappear — but will become a part of everyday workflows."
As built-in prompt assistants and auto-optimization features become standard in leading platforms, much of the “heavy lifting” behind prompt engineering will happen behind the scenes. AI tools will suggest, refine and even test prompts on the fly, making it easier for anyone — regardless of technical skill — to guide models effectively.
